How to Get Rid of White Spots From Tanning
White spots found on the skin appear for many reasons, such as mycosis and other skin problems like dermatitis, hypomelanosis or vitiligo.
When a spot appears on your skin, you should take note of its size, its location, when it appeared and if you have any other symptoms, such as itching, dry skin or peeling. You should then book an appointment with a dermatologist for assessment and to start treatment if indicated.
Some possible causes of white spots or patches on the skin and their treatment include:
1. Mycosis
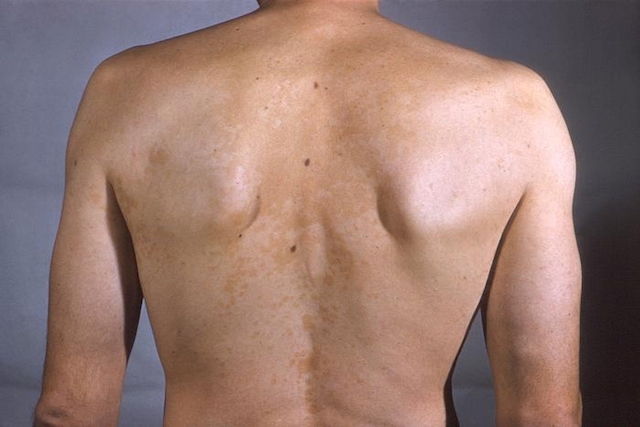
Mycosis
One of the most common causes of small white spots on the skin is mycosis, which is a fungal infection also known as pityriasis versicolor or tinea versicolor. These spots can be very itchy and can spread to other areas of the body
It is sometimes called "beach" mycosis, as the white spots become more pronounced when skin becomes tanned from the sun. The fungus that causes this mycosis is actually naturally found on the skin, but it can over-multiply and form spots on the neck, trunk or back.
What to do: Apply antifungal ointment as prescribed by a dermatologist, (e.g. isoconazole, ketoconazole or miconazole). Shampoo, soaps and gels may also be indicated to supplement the treatment. To protect other people in the house from infection, each person should use their own bath towel and avoid sharing clothes.
2. Peeling from sun exposure
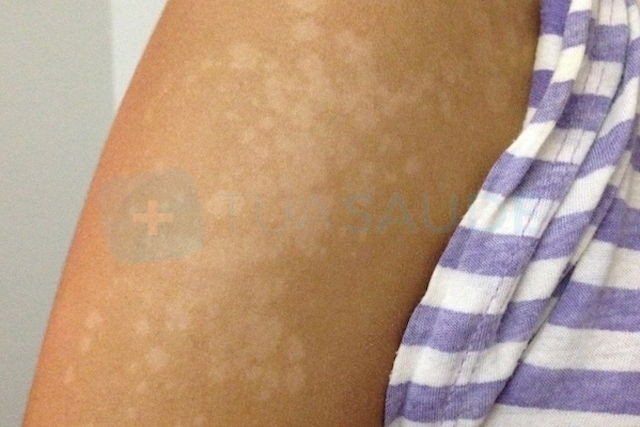
White spots caused by sun exposure
It is typical for people with lighter or olive skin to get tanned after spending a day at the beach or pool, but with excessive sun exposure, skin can peel a few days later. Skin that has peeled can cause small white patches to appear, especially on the arms, chest and back.
What to do: It is important to moisturize your skin daily, and to always apply sunscreen before going into the sun. Skin that is thinner or more sensitive has a higher risk of being sunburnt. Ideally, you should moisturize your skin thoroughly for about 10 days before a day in the sun. Foods that are high in vitamin A (like carrots, tomatoes, boiled eggs, papaya and mangos) can also help to prevent sunburns. The more hydrated the skin is, the lower the risk of peeling and developing blemishes.
3. Atopic dermatitis or atopic eczema
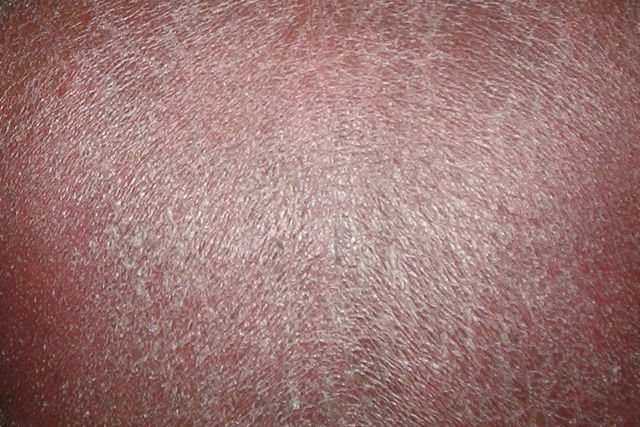
Atopic dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis is an inflammation of the skin that appears mostly in babies, but it can appear at any age. Dermatitis generally causes red patches, bumps or lumps, but when they disappear, they can make the skin area look whiter.
What to do: The usual treatment is steroid medication prescribed by a dermatologist twice a day. The skin should also be kept hydrated, and a antihistamine may be recommended to relieve any itching.
4. White freckles
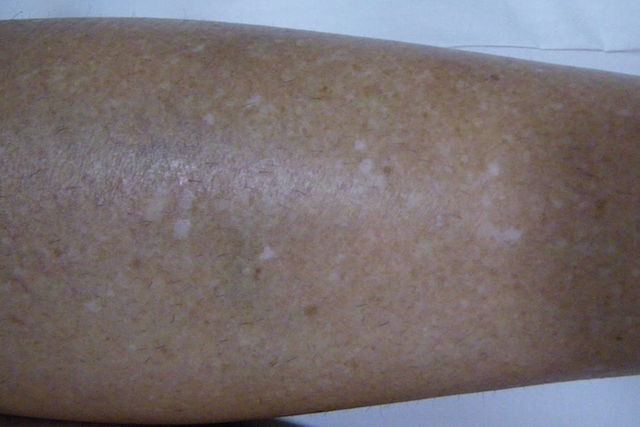
White freckles on the leg
Lighter-skinned people, especially over the age of 40, can develop several small white freckles that may appear on the hands, arms or legs. This usually happens in people with fair skin or who have been exposed to the sun for many years without sunscreen.
What to do: It is recommended that you protect your skin from the sun by always using sunscreen when you go to the beach or pool, or whenever you spend more than 15 minutes out in the sun. Wearing a hat and gloves can also be helpful in preventing the sun's rays from causing skin lesions.
5. Vitiligo
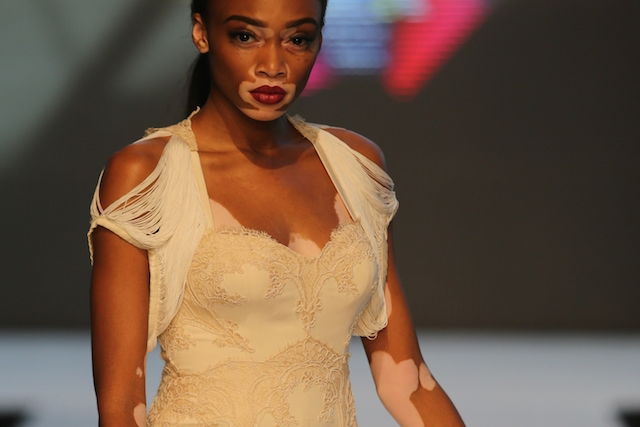

Vitiligo on the face, chest and arms
This is a disease which causes the appearance of large white patches on the skin or even inside of the mouth. Its cause isn't fully understood, but is believed to occur due to a genetic mutation or due to an autoimmune disorder in which your body starts to attack its own melanocytes.
What to do: The doctor can indicate treatment like phototherapy, and medications like corticosteroids or immunosuppressants. One of the drugs that may be indicated is Melagenina plus, which stimulates the production of melanocytes and melanin to even out skin tone.
6. Hypomelanosis
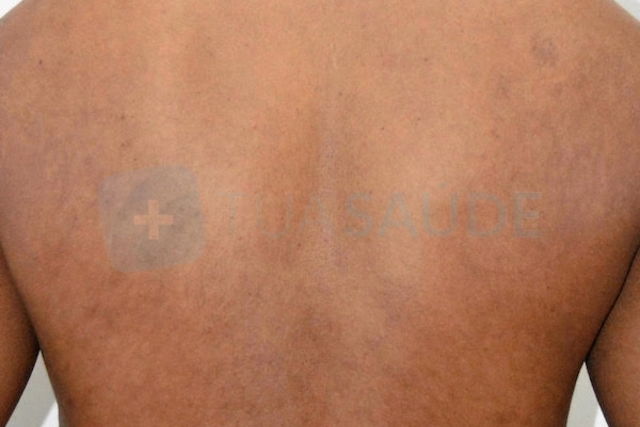
Hypomelanosis
Hypomelanosis is a skin condition in which some parts of the body appear to be lighter than the person's overall skin tone. Affected skin can improve with sun exposure, but it will generally be lighter than the rest of the body. This skin change is more commonly seen in people with allergies.
What to do: Although you don't need any specific treatment, sun exposure early in the morning or in the late afternoon may be helpful in trying to even out your skin tone.
7. Tuberous sclerosis
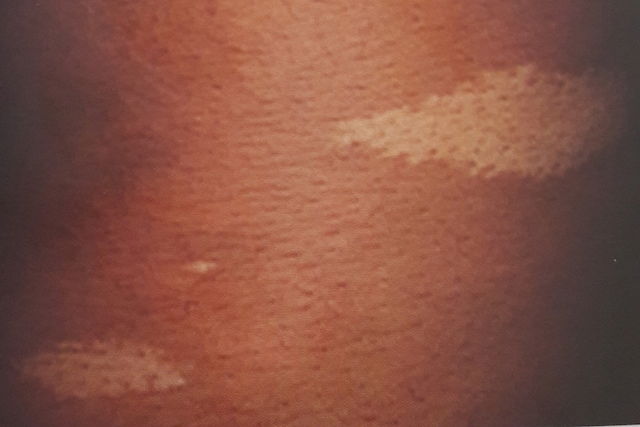
Tuberous sclerosis in children
Also known as Bourneville disease, tuberous sclerosis is characterized by the appearance of white patches that are scattered throughout the body (although they are most commonly found around the trunk). These patches are often first seen in infants or children up to the age of 6, and can appear in various quantities (ie. just one patch or over a hundred).
What to do:You should see a dermatologist to confirm the diagnosis and start treatment to avoid any complications, such as seizures or even kidney problems.
Can white spots be cancer?
White spots with uneven edges and different textures or colours can be a sign of non-melanoma skin cancer. If you have any concerns, consult a dermatologist for assessment and possible treatment.
Can white spots be caused by worms?
With a worm infection, it is possible to have an impairment in the absorption of vitamins and nutrients through digestion, and this can cause white spot on the skin. However, white spots do not always appear with worm infections. Some food can also cause white spots on the skin, especially those with calcium, vitamin D and vitamin E, like milk, sardines, butter and peanuts.
If the cause of white spots on the skin is actually a worm infection, this should be confirmed with a stool sample so that treatment can be initiated.
How to Get Rid of White Spots From Tanning
Source: https://www.tuasaude.com/en/white-spots-on-skin/